Today’s dominant internet platforms are built on aggregating users and user data. As these platforms have grown, so has their ability to provide value — thanks to the power of network effects — which has enabled them to stay ahead.
For example, Facebook’s (now Meta’s) data on user behavior helped it fine-tune its algorithms to a point that its content feed and ad targeting were dramatically better than what competitors could offer. Amazon, meanwhile, has exploited its broad view into customer demand to both optimize delivery logistics and develop its own product lines. And YouTube has built a massive library of videos from a wide array of creators, enabling it to offer viewers content on almost any topic.
In these business models, locking in users and their data is a key source of competitive advantage. As a result, traditional internet platforms typically do not share data even in aggregate — and they make it difficult for users to export their social graphs and other content. So, even if users grow dissatisfied with a given platform, it’s often not worth it to leave.
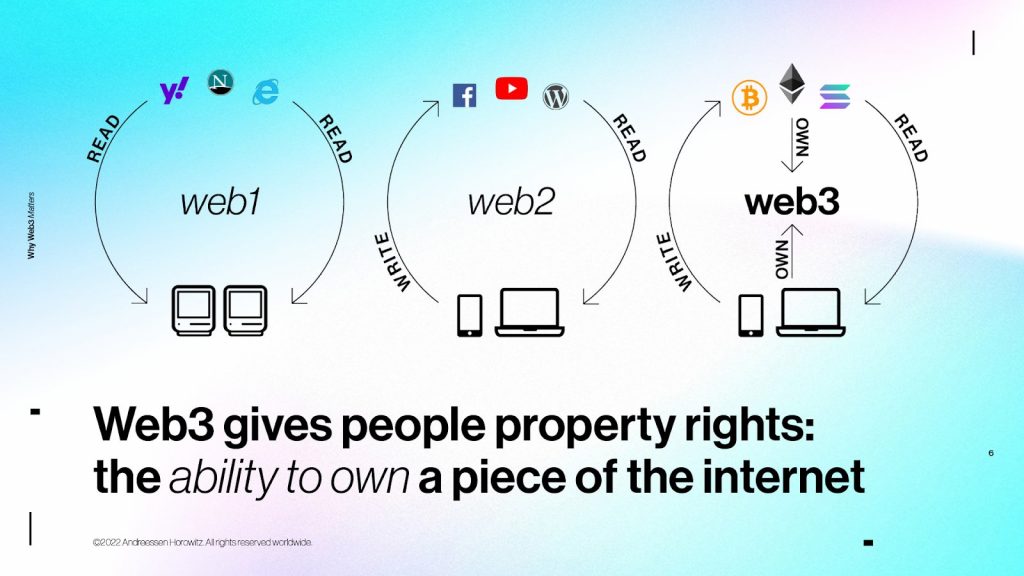
But all of this might be changing. While it’s hard for newcomers to challenge “Web 2.0” companies like Meta on their own terms, now companies — working in what they’re calling a “Web3” model — are proposing a novel value proposition.
Despite all the public conversations around the metaverse and various hyper-financialized NFT projects, Web3, more than anything, is a fundamentally different approach that some developers have agreed to. It’s based on the premise that there’s an alternative to exploiting users for data to make money — and that instead, building open platforms that share value with users directly will create more value for everyone, including the platform.
In Web3, instead of platforms having full control of the underlying data, users typically own whatever content they have created (such as posts or videos), as well as digital objects they have purchased.
Moreover, these digital assets are typically created according to interoperable standards on public blockchains, instead of being privately hosted on a company’s servers. This makes the assets “portable,” in the sense that a user can, in principle, leave any given platform whenever they want by unplugging from that app and moving — along with their data — to another one.
Why Build in Web3
.
—–